
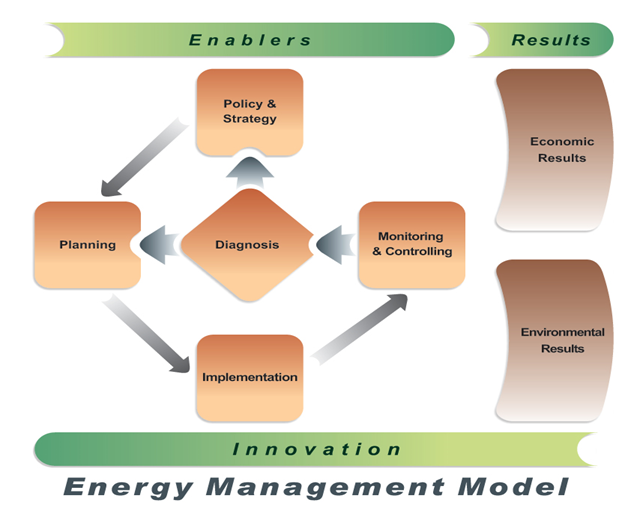
Energy Management Model
Energy Management Model is a framework based on seven criteria; five of them are enabler and the other two are the results acquired by the organization. The enablers are the cause of results and the feedback helps improve results.
Based on this model, the economic and environmental results of implementation of energy management model are achieved systematically. They include development and institutionalization of diagnosis, policy and strategy, planning, deployment as well as monitoring and control of results.
Since this model has a sound management system approach, all criteria are interlinked and interdependent either directly or indirectly. The following image illustrates interrelationship between results and enablers of the model.
The seven-criterion model illustrates the requirements for the implementation of energy management system and progress in sustainable development. Each criterion is supported by a number of sub-criteria throughout implementation.
The objective behind adopting energy management model approach is to make sure about the installation of systems and processes required for energy efficiency, energy use and consumption with a view to reducing costs as well as the environmental and greenhouse gas effects through systematic management.
Under this model, legal requirements must be seriously taken into account. Energy refers to electricity, fuel, steam, heat, compressed air and similar carriers.
- Diagnosis
The performance of energy management system depends on a precise knowledge of aspects of the activities of the organization, which will affect the environment and the economy. The diagnosis criterion is very important in the implementation of energy management system. Diagnosis presents an image of the “footprint of the environment and the economy” in the organization and sets the stage for development, implementation, persistent improvement as well as energy management strategy through quantitative and qualitative objectives. The sub-criteria for diagnosis are as follows:
- Analysis of Energy Efficiency, Use and Consumption
- Defining energy management domain
- Preparing a list of equipment and technology
- Identifying energy consumption by equipment and technology
- Identifying minor and major objectives of energy in the organization
- Developing a method for assessment of results in specified timeframe
- Working out mechanism to control factors affecting efficiency, use and consumption
- Defining the necessary criteria and methods for implementing and controlling energy management system
- Gathering data and their analysis
- Determining energy base line
- Approval and endorsement of properties of method of execution, instructions and documents in all procedures
- Energy Analysis in Production
- Measuring the amount and cost of energy consumption in the process of production
- Identification of all variables in the analysis of data
- Gathering data for comparison with better standards or organizations
- Systematic Execution of “Diagnosis” in Energy Management
- “Diagnosis” before execution of energy management system
- Implementation, revision and upgrading of “diagnosis” throughout execution
- Planning and dissemination of information about execution of energy management “diagnosis” in the organization
- Team building for the execution of “diagnosis” and relevant activities
- Drafting a dynamic report containing background on energy management “diagnosis”
- Energy Management Strategy and Policy
Energy management policy and strategy are not only indicative of the management’s commitment to implementing energy management system, but also includes the organization’s obligation for executing the philosophy of energy management (energy efficiency, use and consumption) in full conformity with legal requirements. Furthermore, the policy and strategy for energy management must be documentable, executive, protectable, improvable and open to criticism so that it could be considered as a framework for the institutionalization of objectives.
- Energy Management Inclusiveness Guarantee
- Pledging commitment to objectives of the organization for executing energy management system
- Pledging commitment to legal obligations for energy management
- Pledging commitment to preventing and reducing the effects of energy use and consumption on the environment
- Pledging commitment to defining plan for improving energy performance (energy efficiency, use and consumption)
- Pledging commitment to the accessibility of resources and data for achieving minor and major objectives
- Pledging commitment to the purchase of energy-efficient products
- Development, Employment, Revision and Updating of Energy Management Strategy
- Development of energy management system through improvement, employment, revision and updating of energy management strategy
- Development of energy management strategy based on energy efficiency, use and consumption
- Identification and understanding of effects of all environmental aspects in “diagnosis” with regards to the strategic elements of energy management
- Employment of energy management strategy based on the size and properties of the organization and its activities
- Development of the transparent objectives of energy management strategy to be understandable, reliable and meaningful for all
- Revision and updating of requirements, objectives and approaches of energy management strategy
- Contribution of staff to development, employment, revision and updating of energy management strategy
- Promoting Energy Management Policy and Strategy
- Extension of energy management system and philosophy to all levels of the organization
- Definition and/or documentation of energy management policy and strategy
- Transparent presentation of energy management policy and strategy in the organization
- Making sure that all staff are familiar with the policy and strategy and any possible change
- Spreading energy management policy and strategy to all beneficiaries and across the society
- Energy Planning
Energy management system requires sound planning for development and execution of transparent quantitative and qualitative objectives. This planning is required to be based on systematic diagnosis and revision, legal requirements and monitoring.
- Systematic Identification of Legal Requirements
- Systematic identification and updating of all energy-related legal requirements (efficiency, use and consumption)
- Filing documented reports on all legal requirements
- Systematic revision of all activities related to legal requirements
- Revision, Employment and Development of Energy Management Plans
- Measurement of energy use and consumption in the past and present
- Adoption of energy management plan as a framework for developing and updating objectives
- Benefiting from achievements of “diagnosis” and “legal requirements” with a view to drawing up and updating energy plan
- Drawing up, employment and updating of the plan (before measurement and drafting work progress report) based on environmental requirements
- Identification of function indicators for measuring the quantitative and qualitative objectives of realization of the plan
- Prioritization of energy management measures
- Technical, economic, legal and organizational assessment as well as financial feasibility of energy management
- Structure of Energy Management Plans
- Development and employment of plan by determining
- Energy management option
- Objectives of execution of options
- Benefits expected from implementation of objectives
- Timeframe of execution
- Timeframe of realizing objectives of plan
- Budgeting
- Necessary training for staff
- Methods of implementation
- Energy Management Implementation
Implementation of energy management is to put into action energy management strategy and plan. It involves all activities related to energy management for achieving predetermined objectives, and has to follow all instructions including technical reports and plans. Superior organizations implement energy management more effectively and more systematically. Here are sub-criteria related to energy management implementation:
- Effective Energy Management Implementation
- Formation of an active “diagnosis” team for energy management
- Making sure that the team has undergone the necessary energy management training and is equipped with up-to-date knowledge about energy management
- Identification of all technical details of energy management options
- Calculation of all benefits expected from the implementation of options and expressing the effect of options on the objectives of the plan
- Preparing the necessary documentation
- Filing all technical reports or other necessary details
- Identification of executive obstacles to energy management and offering solutions
- Implementation of energy management based on indicators mentioned in the technical report and perceived plan
- Assurances about sufficient technical, financial and human resources for implementation
- Continuous revision of the process of implementation
- Preparation for any possibility of changes in the implementation
- Strategic planning
- Clarifying Implementation Tasks
- Making sure that all individuals tasked with implementation have the necessary knowledge and preparation and sufficient time to accomplish their task
- Making sure that all individuals involved in the implementation of energy management have received sufficient training
- Communications in Energy Management Implementation
- Making sure that everyone is well aware of his own and others’ role in the implementation of energy management system
- Organizing meetings for staff
- Monitoring and Control
Any plan that could not be monitored will be unmanageable. Assessment of results will make it possible to control all executive activities, effectiveness and follow-up on environmental and economic objectives in the organization. Moreover, monitoring facilitates updating diagnosis, policy and strategy, planning and systematic execution of energy management.
Here are sub-criteria for monitoring and control:
- Systematic and Appropriate Implementation of Monitoring and Control
- Determining the period and method of monitoring and control of all results achieved from energy management options (measurement period must be precise and sufficient)
- Using monitoring methods appropriate for measurement (these methods must be updated continuously)
- Using appropriate and calibrated equipment for monitoring and control
- Recording and reporting all results achieved from monitoring
- Assessment of Monitoring and Control Results
- Calculation of changes in the energy efficiency and consumption (both are causes of energy management implementation)
- Calculation of saved energy due to energy management
- Calculation of performance indicators for assessing the effectiveness of executive activities
- Level of realization of the plan’s objectives
- If necessary, choosing criteria to compare performance with other companies to make sure about the appropriateness of decisions
- Recording and reporting all achievements and analyses
- Application of Monitoring and Control Report for Improvement
- Making sure that the monitoring and control results are used for preventing deviation from objectives and updating (continuous improvement).
- Making sure that the results of monitoring and control are used in “diagnosis” follow-ups on energy management.
- Environmental Results
The organization achieves significant results by respecting the environment like reducing pollution. Such an approach will boost competitiveness, productivity and the prestige of the organization among others. The environmental results are related to boosting energy efficiency as well as its use and consumption. Key environmental factors are used to assess the environmental results related to enablers in the energy management model.
- Key Consumption Indicators
- Electricity
- Thermal energy
- Compressed air and heat
- Fuel/energy carriers
- Pollution Indicators
- Air (greenhouse gas generation)
- Other possible pollutions
- Economic Results
With efficient energy use, pollution declines and implementation of energy management model will bring economic benefits for the organization and will boost their power of competition. The economic results expected from the implementation of energy management must be defined within the framework of the organization’s energy management policy and strategy. To that effect, key factors of economic performance related to enablers are measured.
- Economic Performance Indicators
Some key indicators of economic performance are directly related to the objectives perused by the organization’s energy management and they may be used in assessment of economic assets. They are as follows:
- Return of investment made in energy management
- Reimbursement timeframe
- Improvement projects implementation costs
- Maintenance costs
- Production Performance Indicators
- Production quality
- Energy efficiency
- Energy use and consumption
