
HSE Maturity Label
Health, Safety & Environment Model
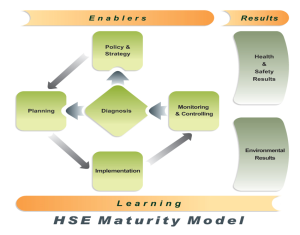
HSE Maturity Label is a seven-criterion framework, five of which are enabler and the other two are the results acquired by the organization. The enablers are the cause of results and the feedback helps improve results.
Based on this model, the health, safety and environmental results of implementation of HSE model are achieved systematically. They include development and institutionalization of diagnosis, policy and strategy, planning, deployment as well as monitoring and control of results.
Since this model has a sound management system approach, all criteria are interlinked and interdependent either directly or indirectly. The following image illustrates interrelationship between results and enablers of the model.
The seven-criterion model illustrates the requirements for the implementation of HSE system and progress in sustainable development. Each criterion is supported by a number of sub-criteria throughout implementation.
- Diagnosis
The performance of HSE system depends on precise knowledge about aspects of the organization which affects the environment, safety and health. Diagnosis is a significant criterion in the HSE model for implementing and improving the system. Diagnosis presents an image of the “footprint of the environment, safety and health” in the organization, which sets the foundation for development, implementation, continuous improvement, policy and strategy through quantitative and qualitative objectives. Here are sub-criteria for diagnosis:
- Analysis of Processes
- All activities and objectives of processes are specified.
- Variable factors (environment, safety, health) are specified.
- The control system of variable factors is specified.
- A list of equipment and technology is drawn up and their roles in the processes are specified.
- Properties of executive methods, instructions and all documents are approved and endorsed.
1.2. Professional Health and Industrial Safety Analysis
- Gathering information and analyzing damage/accidents in workplaces
- Analyzing potential dangers to health in workplaces
- Reducing, preventing or controlling dangers
- Analyzing staff and neighbors’ complaints and satisfaction
1.3. Products and Materials Analysis
- An inventory of products, materials and their information is made.
- The amount and cost of products and materials are determined.
- Studies are conducted on water consumption and supply costs.
- Studies are conducted on energy consumption costs.
- Studies are conducted on thermal energy consumption costs.
- All variables and trends are taken into account in data analysis.
- Equilibrium is taken into account in material consumption.
1.4. Analysis of Emissions
- Studying wastewater pollution
- Studying air pollution
- Studying soil pollution
- Studying noise pollution
1.5. Continuous and Systematic Execution of Diagnosis in HSE
- “Diagnosis” before HSE implementation
- Implementation, revision and continuous updating of HSE system throughout execution
- Planning and dissemination of information about HSE diagnosis in the organization
- Team-building for “diagnosis” and all relevant activities
- Recording reports of HSE “diagnosis”
- HSE Policy and Strategy
HSE policy and strategy are not only indicative of the management’s commitment to implementing the system, but also includes the organization’s obligation for executing the philosophy of HSE with the contribution of all beneficiaries and in full conformity with legal requirements. Furthermore, the policy and strategy for HSE must be documentable, executive, protectable, improvable and open to criticism so that it could be considered as a framework for the institutionalization of objectives.
2.1. Guaranteeing Inclusiveness of HSE Policy
- HSE policy explains the commitment and objectives of the organization for implementing HSE system.
- HSE policy elucidates the legal requirements for safety, health and environment.
- HSE policy indicates commitment to preventing and reducing destructive impacts on the environment and improving health and safety of staff.
- HSE policy includes commitment to a plan for improving the environmental, safety and health aspects.
- HSE policy indicates the organization’s commitment to boost productivity and efficiency in all aspects.
2.2. Development, Implementation, Revision and Updating of HSE Strategy
- Senior management proves its commitment to implementing HSE system through improvement, revision and updating of HSE strategy.
- Development of HSE strategy is based on fundamental concepts
- The effects of all HSE aspects must be understood.
- HSE strategy deployment is in proportion with the size and properties of the organization.
- Deployment of HSE strategy matches the size and features of the organization and results from its activities.
- Development of transparent objectives of HSE strategy, which are comprehensible, reliable and meaningful for everyone
- Revision and updating of requirements, objectives and approaches of HSE strategy
- Contribution of staff in development, deployment, revision and updating of HSE strategy
2.3. Communications in HSE Policy and Strategy
* Extension of HSE system throughout the organization
* Definition and/or documentation of HSE policy and strategy
* Transparent presentation of the HSE policy and strategy in the organization
* Making assurances that all staff are familiar with the strategy and policy and possible changes.
* Spread of HSE policy and strategy to all beneficiaries and the society
- HSE Planning
An HSE system needs sound planning for development and execution of transparent quantitative and qualitative objectives. This planning is required to be based on systematic diagnosis and revision, legal requirements and monitoring.
3.1. Systematic Identification of Legal Requirements
* Systematic identification and updating of all HSE-related legal requirements
* Filing documented reports of legal requirements
* Systematic revision of all activities related to legal requirements
3.2. Revision, Deployment and Development of HSE Plans
* Adoption of HSE plan as a framework in which the objectives (desired environmental, safety and health results) could be developed and updated.
* Using achievements from diagnosis and legal requirements for updating HSE plan
* Drafting, deploying and updating the plan (measurable) based on environmental requirements
* Drafting, deploying and updating the plan (measurable) based on safety and health requirements
* Drafting, deploying and updating the plan (measurable) based on productivity and efficiency requirements
* Identification of performance indicators to measure the quantitative and qualitative objectives of realization of the plan
3.3. Systematic Definition and Assessment of HSE Options
* Establishment of active “diagnosis” HSE team to define HSE options
* Making sure that the team has been trained sufficiently about HSE options and is familiar enough with HSE knowledge
* Identification, development and promotion of options based on HSE philosophy (prevention and reduction) in order to realize the objectives of the plan, i.e.
* Technical, economic, legal and organizational assessment as well as financial feasibility of HSE options
* Identification of all technical details of HSE options and their execution
* Identification of all executive obstacles to HSE options and offering the necessary solutions
* Calculation of desired benefits from execution of options and elucidation of the effect of options on the objectives of the plan
* Filing all technical reports with sufficient explanation
3.4. Systematic and Planned Execution of HSE Pivots
* Development and deployment of the drafted plan for each HSE option which is being implemented like (what job, who, until when, with what resources, which expectations)
– HSE options
– Objectives of execution of options
– Desired benefits
– Deadline for execution
– Deadline for achievement of the plan’s objectives
– Endorsed budgeting
– Providing the necessary training for staff
– Planning and monitoring
- HSE Implementation
Implementation of HSE means realization of HSE strategy and plan, and refers to all activities related to HSE options for the realization of predetermined objectives. It has to follow instructions including technical reports and plans. Superior organizations manage effective and systematic implementation of the plan. Here are the sub-criteria:
4.1. Effective Execution of HSE Options
* Implementation of all HSE options based on indicators mentioned in the technical report and plan
* Assurances about the adequacy of technical, financial and human resources for implementation
* Continuous revision of the process of implementation
* Readiness for any possibility which may change the period of implementation
4.2. Clarification of Implementation Responsibilities
* Making sure that all individuals picked for implementation are ready, have the sufficient knowledge and have enough time to carry out their responsibility
* Making sure that all individuals active throughout the HSE implementation have received enough training
* Organizing meetings for staff
- Monitoring and Control
Any plan that could not be monitored will be unmanageable. Assessment of results will make it possible to control all executive activities, effectiveness and follow-up on environmental and economic objectives in the organization. Moreover, monitoring facilitates updating diagnosis, policy and strategy, planning and systematic execution of HSE.
Here are sub-criteria for monitoring and control:
5.1. Systematic and Appropriate Implementation of Monitoring and Control
Determining the period and method of monitoring and control of all results achieved from HSE options (measurement period must be precise and sufficient)
- Using monitoring methods appropriate for measurement (these methods must be updated continuously)
- Using appropriate and calibrated equipment for monitoring and control
- Recording and reporting all results achieved from monitoring and problems created throughout the process
- Assessment of Monitoring and Control Results
- Calculation of changes in consumption of materials, emissions, process productivity, production, safety and health
- Calculation of saved energy due to HSE option
- Calculation of performance indicators for assessing the effectiveness of executive activities
- Level of realization of the plan’s objectives
- If necessary, choosing criteria to compare performance with other companies to make sure about the appropriateness of decisions
- Recording and reporting all achievements and analyses
- Application of Monitoring and Control Report for Improvement
- Making sure that the monitoring and control results are used for preventing deviation from objectives and updating (continuous improvement).
- Making sure that the results of monitoring and control are used in “diagnosis” follow-ups on HSE.
The organization achieves significant results by respecting the staff and social welfare (health and life quality).
6.1. HSE Key Performance Indicators
These indicators depend on interpretations by staff and people. They are measured through surveys and interviews. These indicators may include the following information:
* Harmful physical factors: noise, temperature, vibration, light, ray, pressure, electromagnetic waves
* Harmful chemical factors: suspended particles (dust, fume, metals, smog), gas, acids
* Harmful ergonomic factors: inappropriate tools, stress, pressure, inconsistency with job, push, cry, loads, solitude
* Psychological factors: fatigue, communications with colleagues
* Mechanical factors: blow, fall of objects, fall of people, electrocution, explosion, unsafe machinery, friction
* Harmful biological factors: virus, bacteria, parasites, fungi
* Staff motivation for HSE
* Staff satisfaction
* Complaints by neighbors
* Job accidents
* Working diseases
* Disease rate
* Potential accidents and traumas rate
* Numerous important accidents
Environmental Results
The organization achieves significant results by respecting the environment like reducing pollution. Such an approach will boost competitiveness, productivity and the prestige of the organization among others. The environmental results are related to consumption of resources as well as spread of pollution. Key environmental factors are used to assess the environmental results related to enablers in HSE model.
. Key Consumption Indicators
* Specified water consumption
* Specified electricity consumption
* Specified thermal energy consumption
* Specified chemical consumption
* Specified fuel consumption
- Key Performance Indicators in Pollution Emission
* Wastewater
* Solid wastes
* Air pollution
* Soil pollution
* Noise pollution
